The stainless steel family
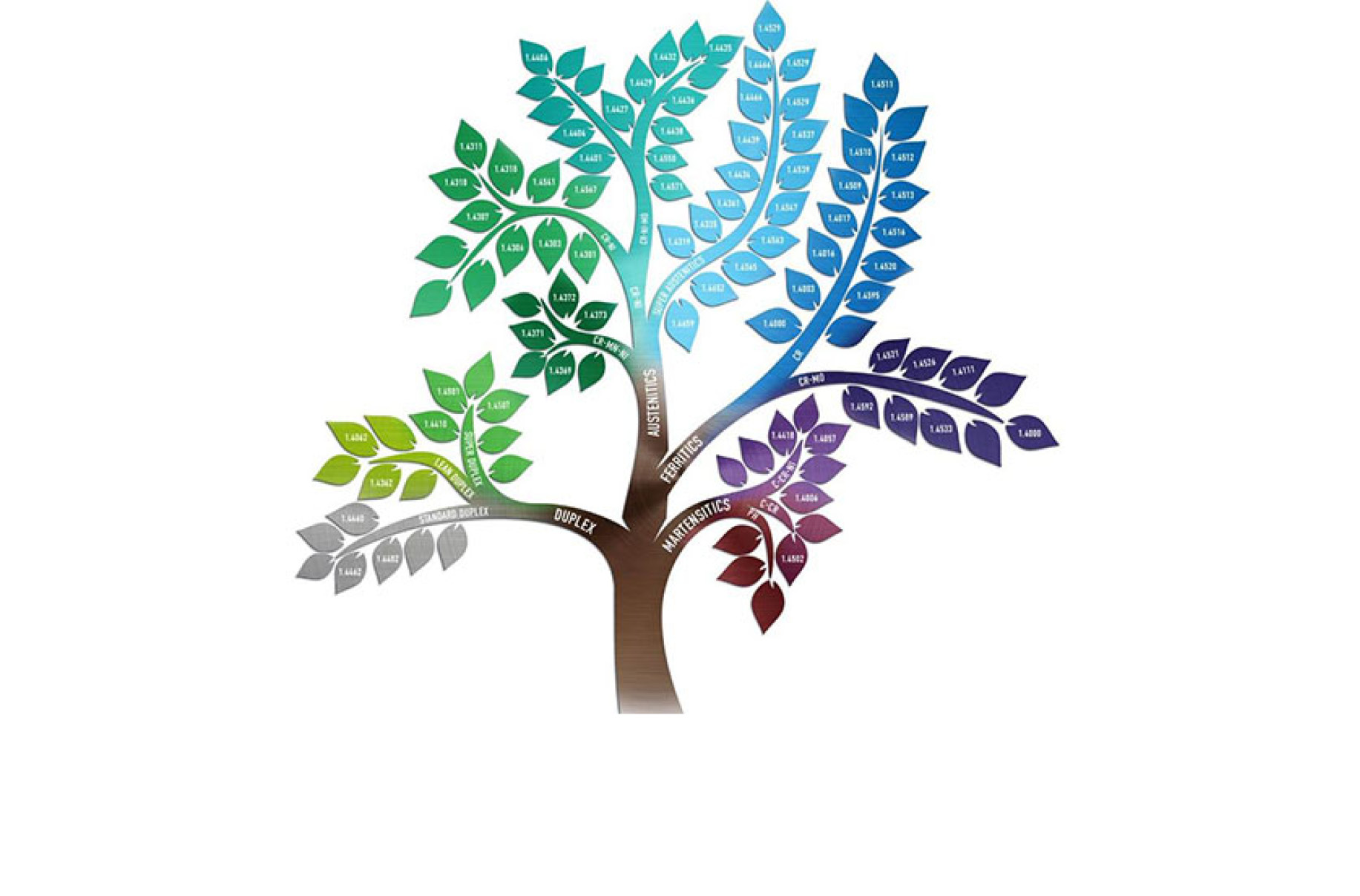

Stainless steel is the generic name for a number of different steels used primarily for their resistance to corrosion. The one key element they all share is a certain minimum percentage (by mass) of chromium: 10.5%. Although other elements, particularly nickel and molybdenum, are added to improve corrosion resistance, chromium is always the deciding factor. The vast majority of steel produced in the world is carbon and alloy steel, with the more expensive stainless steels representing a small, but valuable niche market.
Download more information